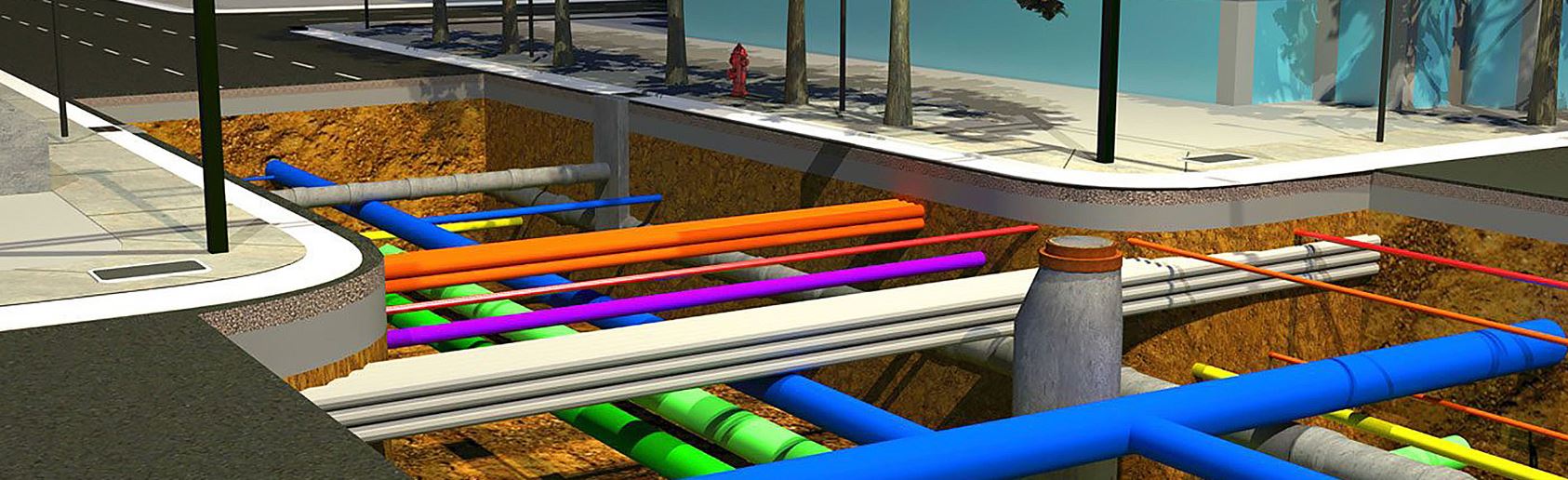
Het detecteren en in kaart brengen van ondergrondse leidingen is een kritische taak die essentieel is voor de veiligheid en efficiëntie van bouwprojecten, infrastructuuronderhoud en stadsplanning. Moderne technologieën zoals warmtecamera’s, grondradar (Ground Penetrating Radar, GPR) en magnetometers spelen een cruciale rol bij het nauwkeurig lokaliseren en identificeren van deze leidingen zonder de noodzaak voor ingrijpende en destructieve graafwerkzaamheden.
Warmtecamera’s
Warmtecamera’s, of infraroodcamera’s, detecteren de warmteafstraling van objecten en kunnen verschillen in temperatuur vastleggen. Wanneer toegepast op het detecteren van ondergrondse leidingen, zijn deze camera’s bijzonder effectief voor het opsporen van warmwaterleidingen en verwarmingssystemen. Het verschil in temperatuur tussen de leiding en de omringende grond maakt het mogelijk om deze leidingen duidelijk in kaart te brengen.
**Voordelen:**
– **Non-invasief:** Er is geen noodzaak om de grond open te breken om de leidingen te detecteren.
– **Snelle detectie:** Warmtecamera’s kunnen snel grote gebieden scannen en onmiddellijke resultaten leveren.
– **Nauwkeurigheid:** Detecteert nauwkeurig leidingen die een temperatuurverschil hebben ten opzichte van de omgeving.
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
GPR is een geofysische methode die gebruik maakt van elektromagnetische straling om ondergrondse objecten te detecteren. Deze technologie is uitermate geschikt voor het identificeren van niet-metalen leidingen, zoals kunststof of beton, die niet door magnetometers kunnen worden opgespoord.
**Voordelen:**
– **Diepe penetratie:** GPR kan verschillende diepten van de ondergrond scannen en een gedetailleerd beeld geven van de ondergrondse infrastructuur.
– **Veelzijdigheid:** Geschikt voor het detecteren van een breed scala aan materialen, waaronder niet-metalen leidingen.
– **Gedetailleerde beeldvorming:** Biedt gedetailleerde en driedimensionale beelden van ondergrondse structuren.
Magnetometers
Magnetometers meten veranderingen in het magnetische veld van de aarde en zijn bijzonder effectief voor het opsporen van metalen leidingen en andere ferromagnetische objecten. Ze kunnen subtiele veranderingen in het magnetische veld detecteren die worden veroorzaakt door de aanwezigheid van metalen objecten onder de grond.
**Voordelen:**
– **Hooggevoelig:** Kan kleine metalen objecten op aanzienlijke diepten detecteren.
– **Nauwkeurig:** Biedt nauwkeurige lokalisatie van metalen leidingen, zelfs in gebieden met veel metalen puin.
– **Non-invasief:** Net als andere detectiemethoden, vereist het geen destructieve graafwerkzaamheden.
Toepassingen en Voordelen van Gecombineerde Technieken
Door de gecombineerde inzet van warmtecamera’s, GPR en magnetometers kunnen professionals een volledig en gedetailleerd beeld krijgen van de ondergrondse infrastructuur. Deze gecombineerde benadering is bijzonder nuttig in stedelijke gebieden waar een complexe mix van verschillende soorten leidingen aanwezig is.
**Voordelen:**
– **Verbeterde nauwkeurigheid:** Het combineren van verschillende detectiemethoden vermindert de kans op fouten en verhoogt de betrouwbaarheid van de resultaten.
– **Comprehensieve analyse:** Biedt een volledig beeld van zowel metalen als niet-metalen leidingen, evenals andere ondergrondse structuren.
– **Kostenbesparend:** Voorkomt onnodige graafwerkzaamheden en minimaliseert schade aan bestaande infrastructuur, wat leidt tot kostenbesparingen.
Het detecteren en in kaart brengen van ondergrondse leidingen met behulp van warmtecamera’s, grondradar en magnetometers is een geavanceerde en efficiënte benadering die de nauwkeurigheid en veiligheid van infrastructurele projecten aanzienlijk verbetert. Door deze technologieën te combineren, kunnen professionals een uitgebreid en betrouwbaar beeld krijgen van ondergrondse leidingen, wat essentieel is voor veilige bouwpraktijken en effectief infrastructuurbeheer. Detectie van nutsleidingen
